Functionality¶
Note that before you can use datasheets you will need to set up your access keys as described in Getting OAuth Credentials.
Workbook Interactions¶
See all workbooks that exist¶
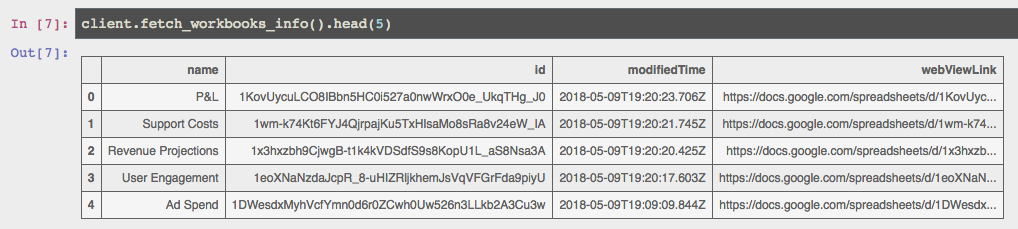
client = datasheets.Client() client.fetch_workbooks_info() # Optionally limit to a specific folder client.fetch_workbooks_info(folder='Finance Reports')This produces a pandas.DataFrame:
See all folders that exist¶
client.fetch_folders() # Optionally limit to only folders you own client.fetch_folders(only_mine=True)
Get a workbook¶
workbook = client.fetch_workbook('Marketing Projections')
Create a workbook¶
client.create_workbook('Q2 Roadmap')
Delete a workbook¶
client.delete_workbook('Q2 Roadmap')
Get a workbook’s URL¶
workbook.url
Tab Interactions¶
See all tabs within a workbook¶
Get a tab¶
workbook.fetch_tab('Radio Spend')
Create a tab¶
workbook.create_tab('Podcast Performance')
Delete a tab¶
workbook.delete_tab('Podcast Performance')
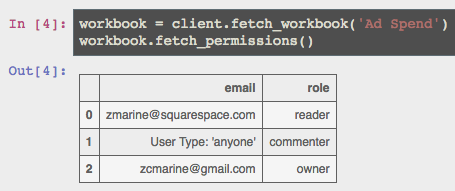
Sharing and Unsharing¶
Data Interactions¶
Get all data in a tab¶
tab = workbook.fetch_tab('Radio Spend') df = tab.fetch_data() # Optionally return a dict of rows, where the keys are the values of the first row of cells data = tab.fetch_data(fmt='dict') # Or return a list of headers (the values of the first row) and a list of rows data = tab.fetch_data(fmt='list')
Add data to a tab¶
# Clear all data in a tab and replace it with a new data set tab.insert_data(df) # Add more data to a tab tab.append_data(df) # For either command, optionally skip uploading the index for the DataFrame tab.insert_data(df, index=False)In addition, by setting
autoformat=Truewithin theinsert_dataorappend_datamethods the data set will be formatted within the tab as shown below: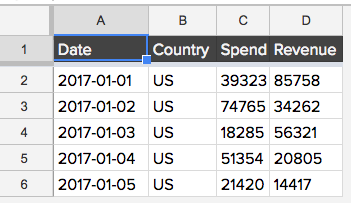
The dimensions of the tab match the data set, the headers are formatted nicely, all cells are left-aligned, and column widths are auto-scaled to fit their contents.
Remove all data from a tab¶
tab.clear_data(df)
Tab Formatting Interactions¶
# Add rows tab.add_rows(30) # Add columns tab.add_columns(5) # Change horizontal and vertical alignment of all cells in tab tab.align_cells(horizontal='LEFT', vertical='MIDDLE') # Alter the number of rows or columns in a tab; if new dimensions are smaller # than current values the tab will be trimmed down to that size tab.alter_dimensions(nrows=25, ncols=10) # Shortcut to color headers dark gray, set all cells to use Proxima Nova size 10, left-align # and middle-align all cells, resize columns to fit their data, and eliminate empty columns # and rows from tab tab.autoformat(n_header_rows=2) # Resize widths of all columns in a tab to fit their data tab.autosize_columns() # Change font and font size for all cells in a tab tab.format_font(font='Proxima Nova', size=10) # Set header rows in a tab to be dark gray with off-white text, font Proxima Nova size 10, # left-aligned and middle-aligned, and rows will be made "frozen" so that when the user # scrolls these rows stay visible tab.format_headers(nrows=3)In addition, anything not explicitly supported by the datasheets library as a stand-alone method can be accomplished using the Workbook.batch_update method and referencing Google Sheets’ spreadsheets.batchUpdate method. More details and an example exist within the docstring for
datasheets.Workbook.batch_update().